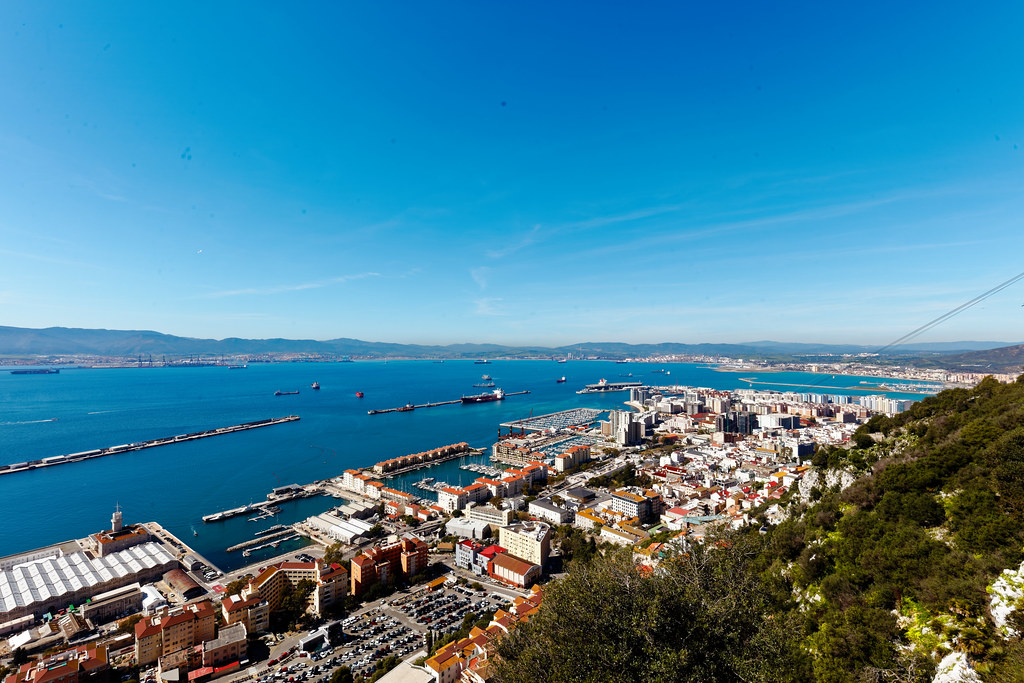
Gibraltar is a British Overseas Territory located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula.
In 1704, Anglo-Dutch forces captured Gibraltar from Spain during the War of the Spanish Succession on behalf of the Habsburg claim to the Spanish throne. The territory was ceded to Great Britain in perpetuity under the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713. During the Napoleonic Wars and World War II it was an important base for the Royal Navy as it controlled the entrance and exit to the Mediterranean Sea (Strait of Gibraltar).

The sovereignty of Gibraltar is a point of contention in Anglo-Spanish relations because Spain asserts a claim to the territory. Gibraltarians rejected proposals for Spanish sovereignty in a 1967 referendum and, in a 2002 referendum, the idea of shared sovereignty was also rejected. On 31 January 2020, the UK and Gibraltar left the European Union. In December 2020, the UK and Spain agreed in principle to a basis on which the UK and the EU might negotiate terms for Gibraltar to participate in aspects of the Schengen Agreement.
The official language of Gibraltar is English and is used by the government and in schools. Most locals are bilingual, also speaking Spanish. Gibraltarians often converse in Llanito a vernacular unique to Gibraltar, based on Andalusian Spanish with a mixture of British English and elements from Maltese, Portuguese, Genoese Italian and Haketia (a Judaeo-Spanish dialect). Llanito also often involves code-switching to English and Spanish. Gibraltarians often call themselves Llanitos.

